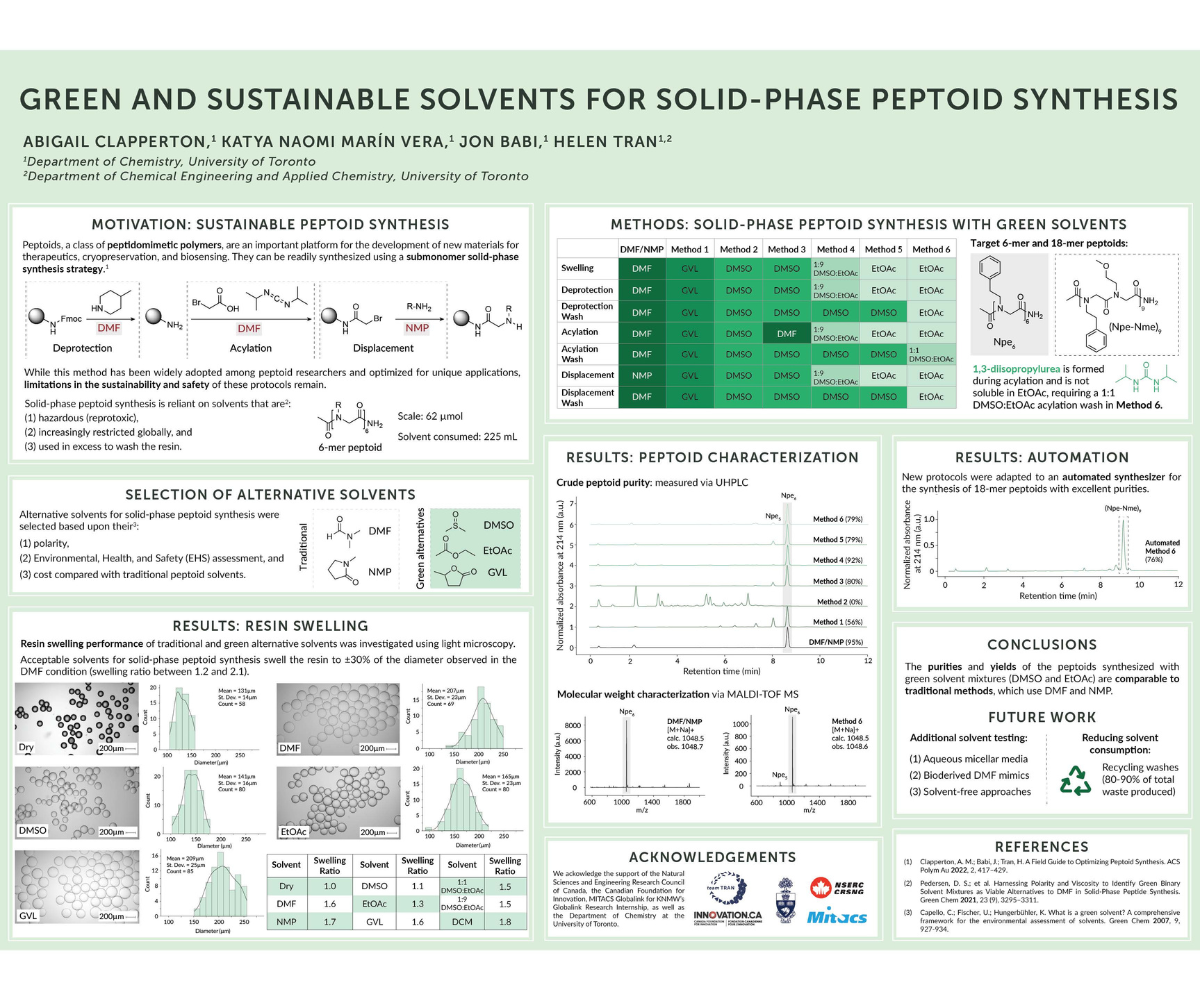
Peptoids, or N-substituted glycine polymers, are an important platform for the development of new materials for therapeutic, cryopreservation, and biosensing applications. The stepwise solid-phase synthesis of peptoids uses iterative acylation and displacement reactions to grow the peptoid chain but relies on hazardous solvents, N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) and N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), which are used in large quantities for resin swelling, washing, and solubilizing the required chemical reagents. With 2 steps required for each monomer addition and repetitive washings following each reaction, there is significant hazardous solvent consumption and waste generation in solid-phase peptoid synthesis. While DMF and NMP have shown excellent performance as peptoid synthesis solvents in both academic and industrial research environments, their use has been restricted by the European Union due to their reprotoxicity. To address the need for solvents with safer profiles, we present the use of green and sustainable solvents and binary solvent mixtures for the solid-phase synthesis of peptoids with adaptations onto an automated synthesizer.