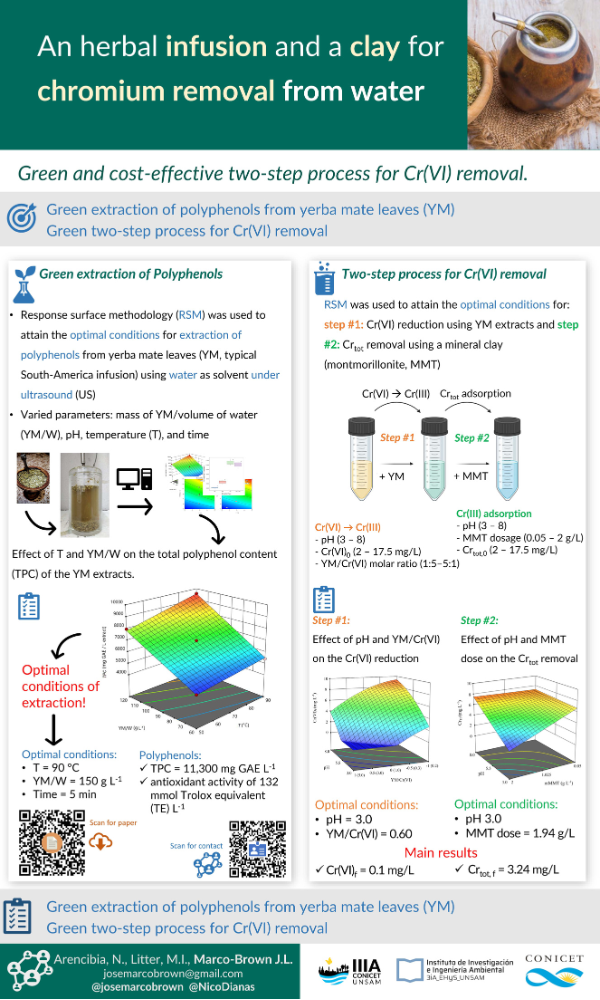
In this work, a response surface methodology (RSM) was used to attain optimal conditions for polyphenols extraction from Yerba Mate (YM, South-America infusion) using water as solvent under ultrasound. The following parameters were varied: mass of YM/volume of water (YM/W), pH, temperature, and time. This study helps to developing an eco-friendly and cost-effective experimental design, reducing the production of wastes, and using a very fast water-based method for the extraction.
Then, a method for the removal of hexavalent chromium from water in two stages with low cost and low environmental impact was developed and optimized. The first stage was based on the reduction of Cr(VI) to Cr(III) using aqueous extract of YM. In this stage, the parameters pH, YM:Cr(VI) molar ratio (RM YM/Cr(VI)) and initial Cr(VI) concentration (Cr(VI)0) were optimized using a RSM. The second stage consisted of the addition of a clay with high montmorillonite (MMT) content as adsorbent and the parameters pH, mass of MMT (mMMT), and initial total chromium (Crtot,0) concentration were optimized.