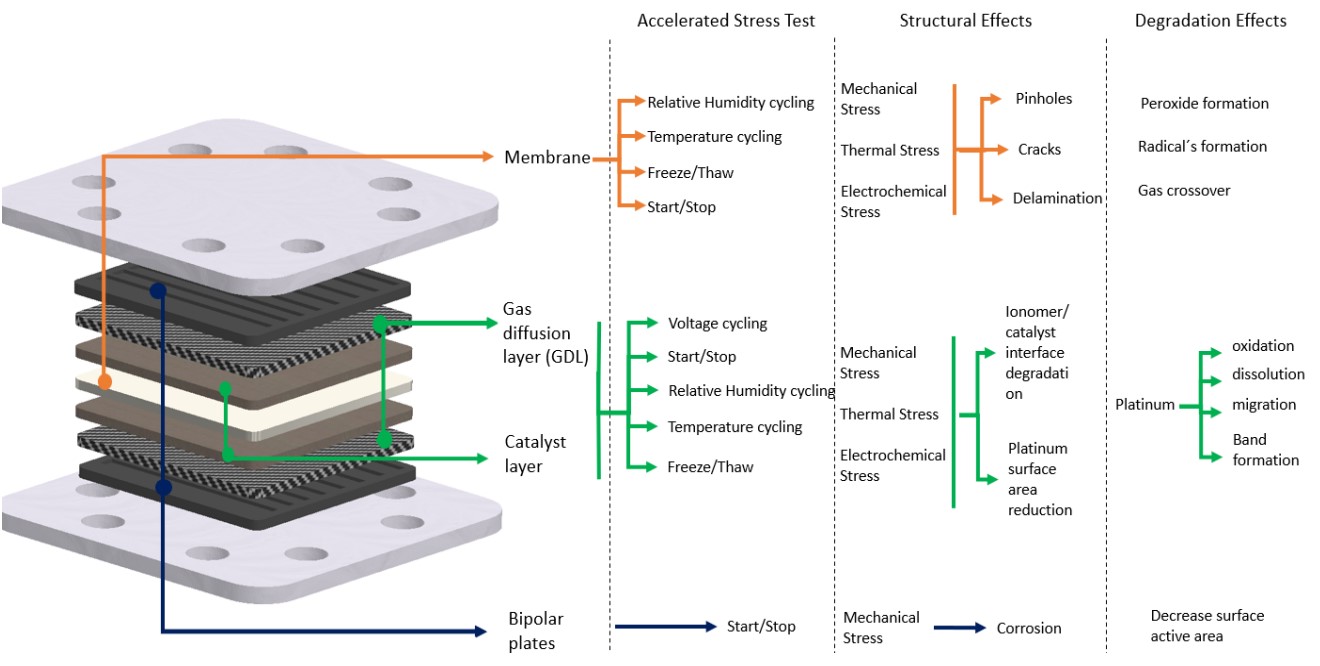
Polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs), considered green devices, use hydrogen and oxygen as reactants in electrochemical processes to produce electricity, water, and heat as by-products. The use of this technology in the automotive industry and power generation has led to a detailed study of its operating principle to make it cost-effective. Polymer electrolyte fuel cells as innovative technology has promoted research to improve its performance. For this reason, a review of the accelerated degradation methods for the membrane, the catalyst layer, the gas diffusion layer, and finally, the bipolar plates are presented. In this work, it also been found that accelerated stress test has already been standardized for cell structure in general however and on the other side there is a little research on degradation methods for bipolar plates. Finally, a brief review of the mitigation strategies has been carried out, given that with the compilation of accelerated aging in the fuel cell structures, it has been observed that the research is focused on improving materials for the use in the layers of fuel cell.