SELECTIVE REMOVAL OF DYES from Water Using Quality-Downgraded Fluorinated Single-walled Carbo Nanotubes
Abstract
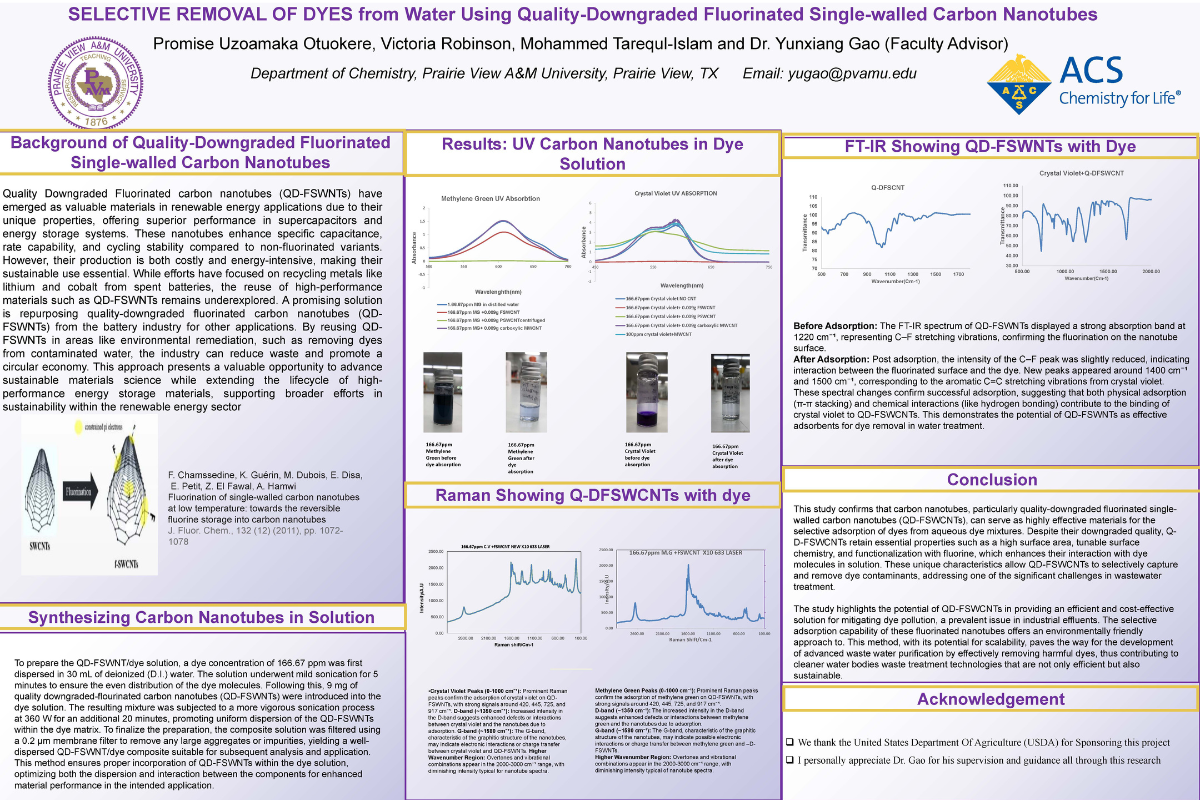
Background and Objective: Highly fluorinated carbon nanotubes emerged as a novel but expensive material for renewable energy applications. Similar to the effort of recycling lithium, its also be beneficial to make use the quality downgraded fluorinated-nanotubes from the battery industry. Other hand, dyes are chemical compounds commonly found in water, which can cause significant environmental pollution and water contamination. Here, we demonstrate that quality-downgraded Fluorinated Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (FSWCNTs), with only contains 1-2% of fluorine, can selectively absorbing and removing dyes from aqueous solutions.
Materials and Methods: In this study, dye concentration was determined using a UV spectrophotometer. A mixture of crystal violet and methylene green dyes was used to evaluate the selective absorption capabilities of different carbon nanotube types, including FSWCNTs, pristine single-walled carbon nanotubes (PSWCNTs), multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), and carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes (Carboxyl-MWCNTs).
Results: The results demonstrated that FSWCNTs effectively and selectively remove crystal violet from the dye mixture in aqueous solutions. Crystal violet was absorbed by FSWCNTs, while PSWCNTs, MWCNTs, and Carboxyl-MWCNTs did not show significant absorption of the dye. This finding highlights the potential of FSWCNTs for selective dye removal in water treatment applications.
Conclusion: This study confirms that carbon nanotubes, particularly FSWCNTs, can be effectively utilized for selective dye absorption from aqueous dye mixtures, offering a promising solution for addressing dye pollution in water.