The exploration of oil in ultra-deep waters (offshore) is crucial due to the high demand for this resource. However, challenges, like the complex task of drilling through salt layers and stringent environmental concerns persist. Drilling fluid plays a fundamental role in the well drilling process, aiding in drill cooling, gravel transportation, and other functions. Although water-based fluids are preferable environmentally, they tend to be less efficient and degrade under high pressures and temperatures.
To tackle this challenge, companies are turning to nanotechnology-based solutions to develop fluids capable of operating efficiently under extreme conditions. One of the primary materials used for this purpose is graphene oxide (GO), known for its exceptional mechanical strength, lubricating properties, and compatibility with water-based fluids. Additionally, GO is chemically stable and can enhance the rheological properties of the fluid.
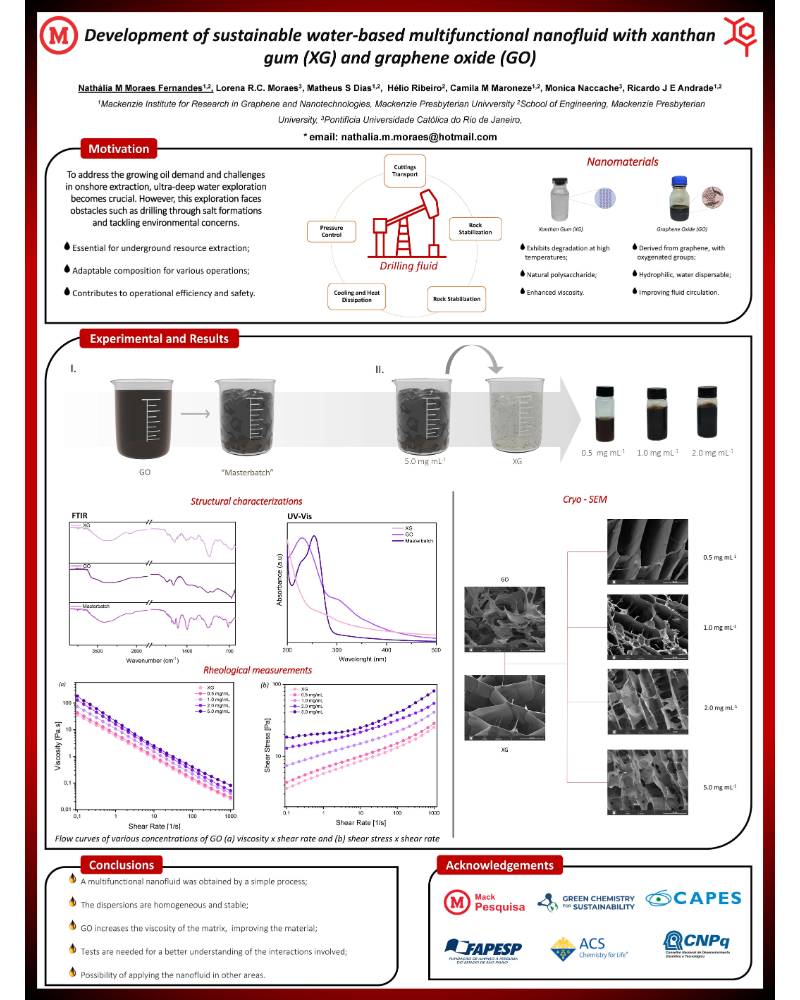
The study focuses on developing and characterizing water-based drilling fluids with GO and xanthan gum (XG), a common biopolymer in the oil industry. A simplified production method was devised, utilizing GO as a filler and XG as a matrix. This method yielded a concentrated dispersion, which was subsequently diluted in the matrix at varying concentrations, facilitating scalable manufacturing.
The light of this approach lies in its focus on water-based fluids as an environmentally sustainable alternative for offshore operations. Implementing these fluids reduces both environmental impact and operational risks.